MCAT Physics Question 79: Answer and Explanation
Home > MCAT Test > MCAT physics practice tests
Test Information
- Use your browser's back button to return to your test results.
- Do more MCAT physics practice tests.
Question: 79
4. A voltaic cell provides a current of 0.5 A when in a circuit with a 3 Ω resistor. If the internal resistance of the cell is 0.1 Ω, what is the voltage across the terminals of the battery when there is no current flowing?
- A. 0.05 V
- B. 1.5 V
- C. 1.505 V
- D. 1.55 V
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
This question tests our understanding of batteries in a circuit. The voltage across the terminals of the battery when there is no current flowing is referred to as the electromotive force (emf or ε of the battery). However, when a current is flowing through the circuit, the voltage across the terminals of the battery is decreased by an amount equal to the current multiplied by the internal resistance of the battery. Mathematically, this is given by the equation
V = ε – irint
To determine the emf of the battery, first calculate the voltage across the battery when the current is flowing. For this, we can use Ohm's law:
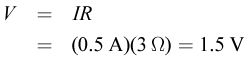
Because we know the internal resistance of the battery, the current, and the voltage, we can calculate the emf:
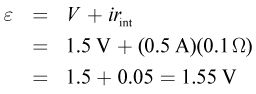
The answer makes sense in the context of a real battery because its internal resistance is supposed to be very small so that the voltage provided to the circuit is as close as possible to the emf of the cell when there is no current running.
