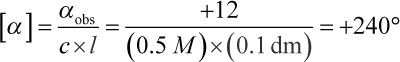MCAT Organic Chemistry Question 27: Answer and Explanation
Home > MCAT Test > MCAT organic chemistry practice tests
Test Information
- Use your browser's back button to return to your test results.
- Do more MCAT organic chemistry practice tests.
Question: 27
12. A scientist takes a 0.5 M solution of an unknown pure dextrorotatory organic molecule and places it in a test tube with a diameter of 1 cm. He observes that a plane of polarized light is rotated 12° under these conditions. What is the specific rotation of this molecule?
- A. –240°
- B. –24°
- C. +24°
- D. +240°
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
Remember that the equation for specific rotation is 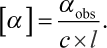 In this example, αobs is +12° (remember that dextrorotatory, or clockwise, rotation is considered positive), c = 0.5 M, l = 1 cm = 0.1 dm. Remember that path length is always measured in decimeters when calculating specific rotation. Therefore, the specific rotation can be calculated as:
In this example, αobs is +12° (remember that dextrorotatory, or clockwise, rotation is considered positive), c = 0.5 M, l = 1 cm = 0.1 dm. Remember that path length is always measured in decimeters when calculating specific rotation. Therefore, the specific rotation can be calculated as: