MCAT General Chemistry Question 195: Answer and Explanation
Home > MCAT Test > MCAT general chemistry practice tests
Test Information
- Use your browser's back button to return to your test results.
- Do more MCAT general chemistry practice tests.
Question: 195
6. Particles with opposite charges attract one another and particles with like charges repel. How can protons, which are positively charged, coexist in the nucleus?
- A. Gravitational forces
- B. Electrostatic forces
- C. London dispersion forces
- D. Strong nuclear forces
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
C For neon to form a solid, there must be intermolecular forces holding the atoms or molecules in relatively fixed positions. Gravitational force is given by F = G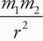 With the constant G on the order of 10-11 and the mass of neon on the order of 10-26, this force is negligible and choice A is eliminated. Electrostatic force is given by F = k
With the constant G on the order of 10-11 and the mass of neon on the order of 10-26, this force is negligible and choice A is eliminated. Electrostatic force is given by F = k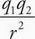 Choice B is incorrect because neon is a neutral atom without any charge, so there are no significant electrostatic forces at play. Choice D is incorrect because strong nuclear forces act over a very small distance essentially limited to the size of the nucleus. Choice C is correct. Neon is a neutral molecule and has induced dipole-dipole interactions, also known as London dispersion forces. Because this is the weakest of the van der Waals forces, neon must be cooled down close to absolute zero before forming a solid.
Choice B is incorrect because neon is a neutral atom without any charge, so there are no significant electrostatic forces at play. Choice D is incorrect because strong nuclear forces act over a very small distance essentially limited to the size of the nucleus. Choice C is correct. Neon is a neutral molecule and has induced dipole-dipole interactions, also known as London dispersion forces. Because this is the weakest of the van der Waals forces, neon must be cooled down close to absolute zero before forming a solid.
