MCAT General Chemistry Question 109: Answer and Explanation
Home > MCAT Test > MCAT general chemistry practice tests
Test Information
- Use your browser's back button to return to your test results.
- Do more MCAT general chemistry practice tests.
Question: 109
4. A 0.040 g piece of magnesium is placed in a beaker of hydrochloric acid. Hydrogen gas is generated according to the following equation:
Mg (s) + 2 HCl (aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)The gas is collected over water at 25°C, and the gauge pressure during the experiment reads 784 mmHg.
The gas displaces a volume of 100 mL. The vapor pressure of water at 25°C is approximately 24.0 mmHg. Based on this data, how many moles of hydrogen are produced in this reaction? (Note:
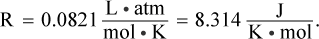
- A. 4.04 × 10-5 moles hydrogen
- B. 4.09 × 10-3 moles hydrogen
- C. 3.07 × 10-2 moles hydrogen
- D. 3.11 moles hydrogen
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
The pressure of the gas is calculated by subtracting the vapor pressure of water from the measured pressure during the experiment: 784 mmHg - 24 mmHg = 760 mmHg, or 1 atm. This is because the reaction is carried out in an aqueous environment; the water present will contribute to the partial pressures of the gas over the liquid. The ideal gas law can be used to calculate the moles of hydrogen gas. The volume of the gas is 0.100 L, the temperature is 298 K, and 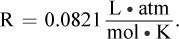 Plugging in, we get:
Plugging in, we get:
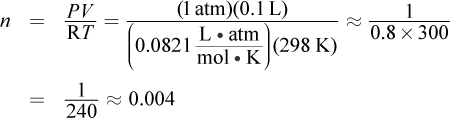
Choice (A) incorrectly substitutes 8.314 into the gas law, rather than 0.0821. Remember that the value of R depends on the other variables in the equation; using 1 atm in the numerator necessitates using 0.0821. Choice (C) incorrectly substitutes the wrong R and keeps the pressure in mmHg. Choice (D) also keeps the pressure in mmHg.
